SynQuE: Estimating Synthetic Dataset Quality Without Annotations
Table of contents
📝 Authors
Arthur Chen & Victor Zhong
arXiv:2511.03928 • Nov 2025
🔗 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.03928
🚀 Overview
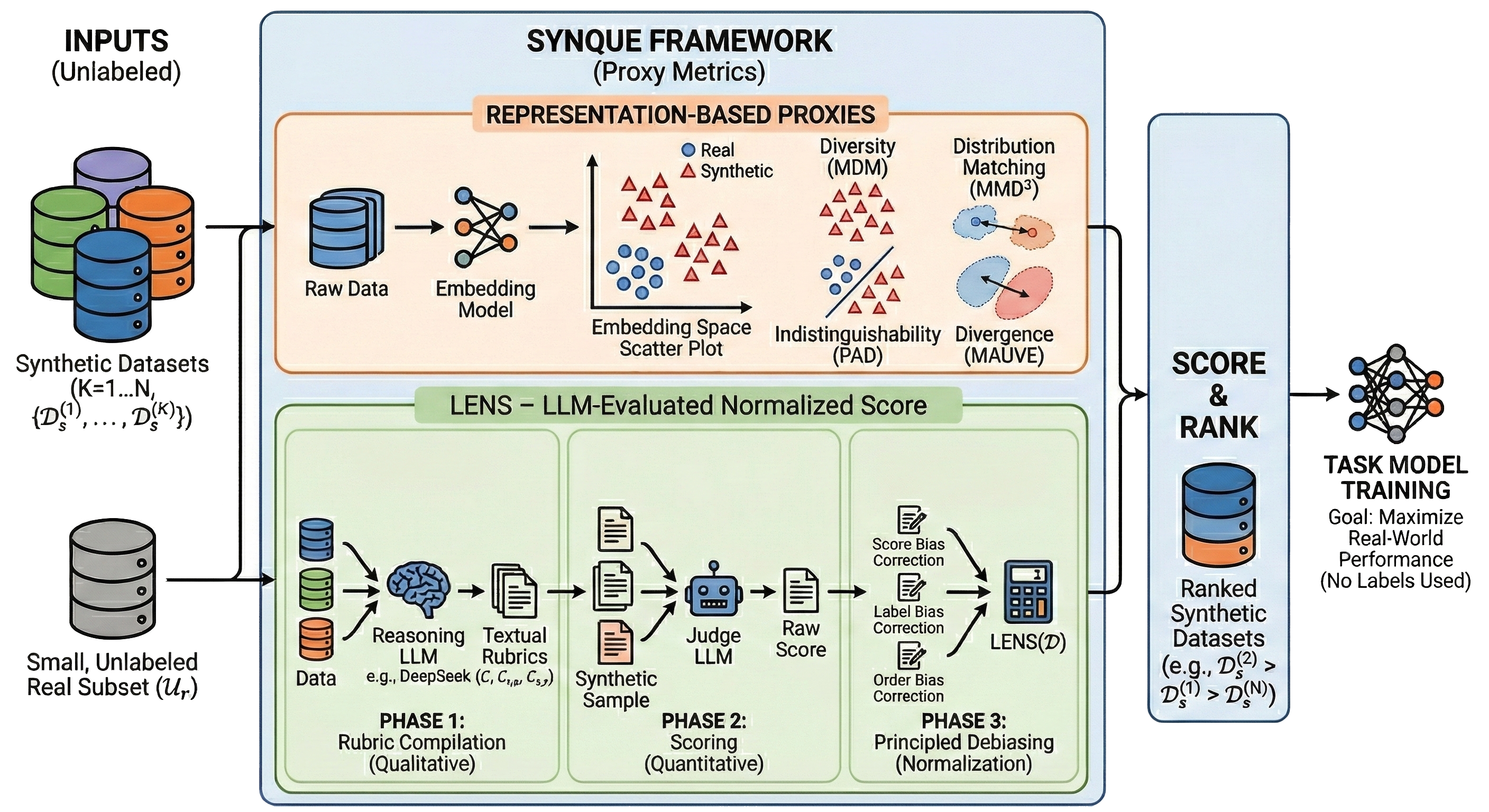
SynQuE (Synthetic Dataset Quality Estimation) is a framework and benchmark for ranking synthetic datasets by their expected real-world performance — without requiring any labeled real data.
This addresses a core bottleneck in data-scarce or privacy-sensitive settings where annotation is expensive or infeasible.
📌 Problem
Synthetic training data generation is widely used, but:
- Not all synthetic datasets are equally useful
- Larger synthetic training datasets do not guarantee better performance
- Selecting high-quality synthetic training data without labels is still unsolved
SynQuE asks:
Can we estimate which synthetic dataset will yield the best real-world performance using only a small amount of unannotated real data?
🧠 Key Contributions
1. Problem Formalization
We formalize SynQuE, a new evaluation setting:
given a pool of synthetic datasets and a small unannotated real dataset, estimate which synthetic dataset will produce the best downstream model performance.
2. Proxy Metrics for Synthetic Data Quality
- LENS (Novel Contribution): We introduce LENS, a principled LLM-based metric that uses reasoning to generate rubrics for distinguishing real and synthetic data. LENS excels at complex, long-horizon tasks (e.g., web navigation) where traditional embedding-based metrics often fail.
- Benchmarking Baselines: We systematically adapt and evaluate standard annotation-free divergence measures (PAD, MMD, Mauve) to the SynQuE setting, establishing strong baselines that remain effective for simpler tasks.
🔍 LENS: LLM-Evaluated Normalized Score
LENS is a reasoning-based synthetic data evaluator that:
- Derives task-relevant rubrics by comparing synthetic and real (unlabeled) data
- Scores synthetic examples using an LLM’s semantic understanding
- Aggregates scores into a dataset-level quality estimate
LENS captures semantic and contextual mismatches that embedding-only metrics often miss, especially in complex reasoning tasks.
📊 Experimental Results
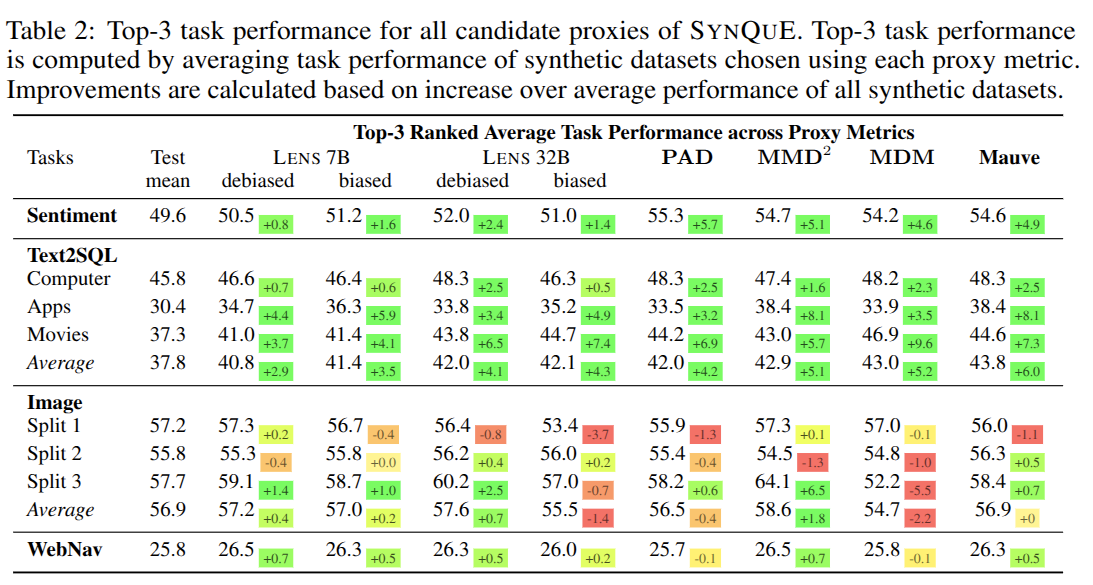
Across diverse tasks, SynQuE shows that:
- Selecting synthetic datasets via SynQuE consistently yields substantial gains over random selection in real-world applications
- Proxy metrics improve downstream performance when trained on top-ranked synthetic datasets compared to random selection
- LENS outperforms embedding-based metrics on long-horizon tasks such as Web Navigation
Example:
On Text-to-SQL, selecting the top-ranked synthetic datasets improves accuracy by ~8 points compared to random selection.
📦 Why SynQuE Matters
SynQuE enables:
- Annotation-free synthetic dataset selection
- More efficient use of synthetic data budgets
- Practical deployment in privacy-sensitive domains (e.g., healthcare, finance)
It is the first benchmark to systematically study synthetic dataset quality estimation without labeled real data.
📎 Resources
- 📄 Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.03928
- 📑 PDF: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.03928.pdf
- 🔗 Code: https://github.com/r2llab/synque
🙌 Acknowledgements
This work was conducted at the University of Waterloo and contributes to bridging the gap between synthetic data generation and real-world model performance evaluation.